on
Semantic Image Search
In the previous post, I described about APIs, HTTP requests and responses using curl. Whereas, in this post we develop an interesting project based on cool web APIs available.
The idea of this project is to simulate Google image search, i.e, query the images based on its content. The important steps for the project are:
- Understand the image content and store it in a database
- Fuzzy search the database
- UI design to show our image gallery
You can preview the end product here.
Understanding the image content
For understanding the image content, there are many computer vision web APIs. These APIs are available as paid version and also for free but limiting number of calls per minute. Among them the popular ones are Microsoft’s Computer Vision API, Google Cloud Vision API and Clarifi Models APIs. The mentioned APIs were developed using cutting-edge technologies like deep neural networks (which results in high accuracies). We use Microsoft Computer Vision API for our project.
To use these APIs in our programming project, we can use open-source modules like requests in Python, request in node.js etc. I chose to use request modules in node.js (javascript). The modules of node.js can be easily installable using npm (node package manager).
Node.js
Node.js is a javascript runtime built on Chrome’s V8 JavaScript engine. It is a powerful framework used for developing I/O intensive web applications. Node.js important features are:
- Event-driven and non-blocking (asynchronous) I/O model
- Lightweight and efficient
- Very fast, single-threaded
- Highly scalable
- No buffering
Coming back to fetching image content, Microsoft(MS) vision API issues a unique subscription key for each user for using their product. Using that subscriptionKey, we can call MS vision API to get the corresponding results for the input images.
//Node.js allows require directive to load its modules
var request = require('request');
const subscriptionKey = <Key given to you>;
const uriBase = 'https://westcentralus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/vision/v2.0/analyze';
//visualfeatures are given in params
const params = {
'visualFeatures': 'Tags,Description,Color',
'language': 'en'
};
const options = {
uri: uriBase,
qs: params,
body: '{"url": ' + '"' + imageUrl + '"}',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key' : subscriptionKey
}
};
//A call back function function is defined to execute once post request is successful
request.post(options, function(error, response, body){
if (error) {
console.error('Error: ', error);
return
}
if(response.statusCode == 200){
let jsonResponse = JSON.parse(body);
console.log(jsonResponse)
}
else {
console.error('Request failed', response.statusCode)
}
});
If you see the above js code, you would have noticed the visual features key in params variable. A very neat description of the visual features is available in this Microsoft vision tutorial. I explained the features that are relevant to our project in the following points.
Input Image:
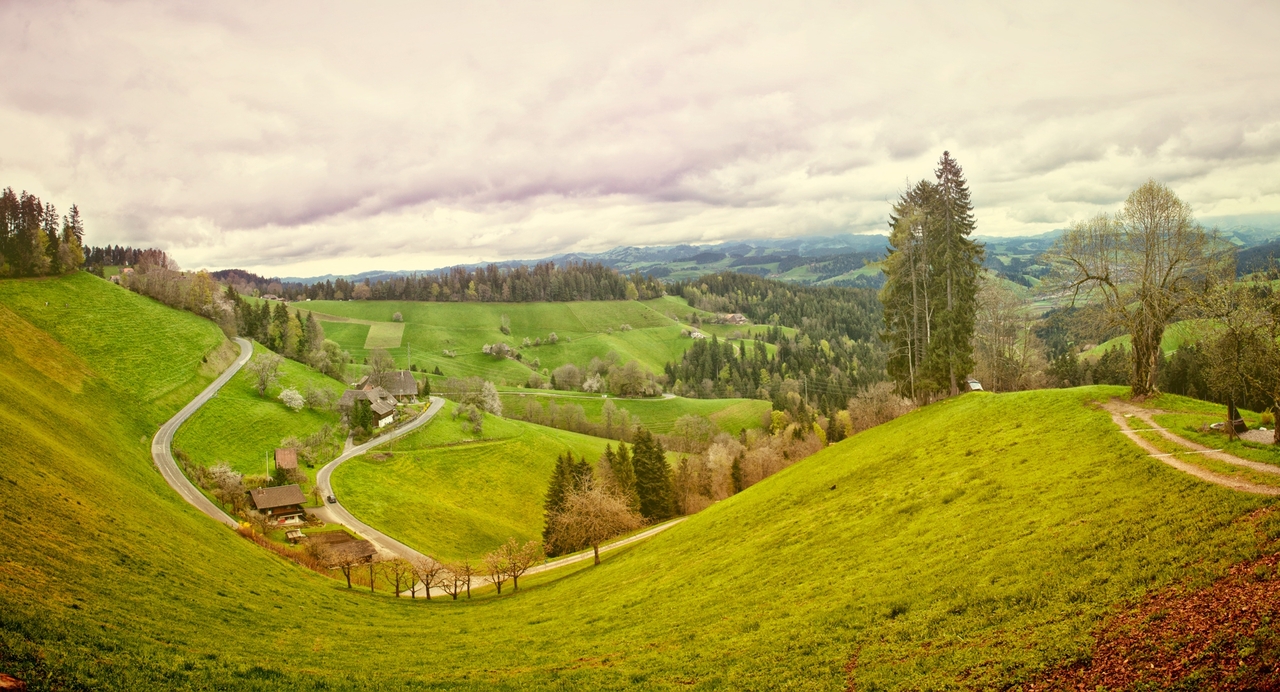

{
"tags": [
{"name": "grass", "confidence": 0.9999996423721313},
{"name": "sky", "confidence": 0.9876105785369873},
...
{"name": "highland", "confidence": 0.0853172242641449}
],
"description": {
"tags": ["grass", "outdoor", ... "horse", "herd"],
"captions": [
{
"text": "a view of a lush green field",
"confidence": 0.8720112217245733
}
]
},
"color": {
"dominantColorForeground": "White",
"dominantColorBackground": "Yellow",
"dominantColors": ["Yellow", "White"],
"accentColor": "BAB30F",
"isBwImg": false
},
"metadata": {"height": 692, "width": 1280, "format": "Jpeg"},
"requestId": "57a3d5d9-3e87-4585-ad13-4b6a74dd955c"
}
Output json
- Tags: This feature recognizes all the objects in the image with a confidence.
- Description: Description was constructed using the neural network model as a human readable sentences with corresponding confidences. For the above image the description created is
a view of lush green fieldwith a confidence of 0.88. - Color: This model detects 3 kinds of colors related to th image. Those are dominant foreground, backround colors as well as accent color.
In the above features, we found the following keys as useful to search a image based on the text pattern accurately.
var searchKeys = [
{name : 'tags.name'},
{name : 'description.captions.text'},
{name : 'color.dominantColors'}
]
As node.js uses asynchronous code execution, there is no straight forward way to force sequential code execution. Hence, callback functions are used to execute the code in synchronous manner. As I am using free trial version which limits number of calls to the API per minute, I couldn’t use typical node.js code. Therefore setting wait time as shown in below code between two API calls makes API usage effectively. The predicted jsonresponses after post request are stored in the database using a module lowdb in js.
for (let i=0; i < images.length; i++){
setTimeout(
function(){
requestVisionAPI(images[i].url);
}, (i+1)*5000);
}
Fuzzy search the databse
Fuzzy string matching is an approximate string matching technique. In java script, fuse.js module is available for finding strings that match a pattern approximately. This module gives many advantages like searching by ID, weighted search, searching in arrays of strings, searching in arrays of objects etc.
Then fuse.js module was used to fuzzy search an input pattern among these json responses. I found the following options are effictive in searching patterns.
function createFuse(images){
var fuse_options = {
shouldSort: true,
threshold: 0.01,
location: 0,
tokenize: true,
distance: 100,
maxPatternLength: 32,
minMatchCharLength: 1,
keys: searchKeys
}
return new Fuse(images, fuse_options)
}
fuse = createFuse(images)
fuse.search(<searchValue>)
UI design
The last task is to present the selected gallery of the images on the page. For this, there is an open source javascript library called nanogallery2. It contains ready to use templates for effective presentation of image gallery on the web pages. We use the following template for the gallery creation.
function createNanoGallery(images){
$("#nanogallery2").nanogallery2({
//gallery settings
"itemsBaseURL": '',
"thumbnailWidth": "auto",
"thumbnailHeight": "400",
"thumbnailBorderVertical": 0,
"thumbnailBorderHorizontal": 0,
"galleryDisplayMode": "moreButton",
"galleryDisplayMoreStep": 4,
"thumbnailAlignment": "center",
"thumbnailHoverEffect2": "imageScaleIn80|labelAppear75",
//gallery content
'items': convertToGalleryList(images)
});
}
The sample view of the page is shown below.
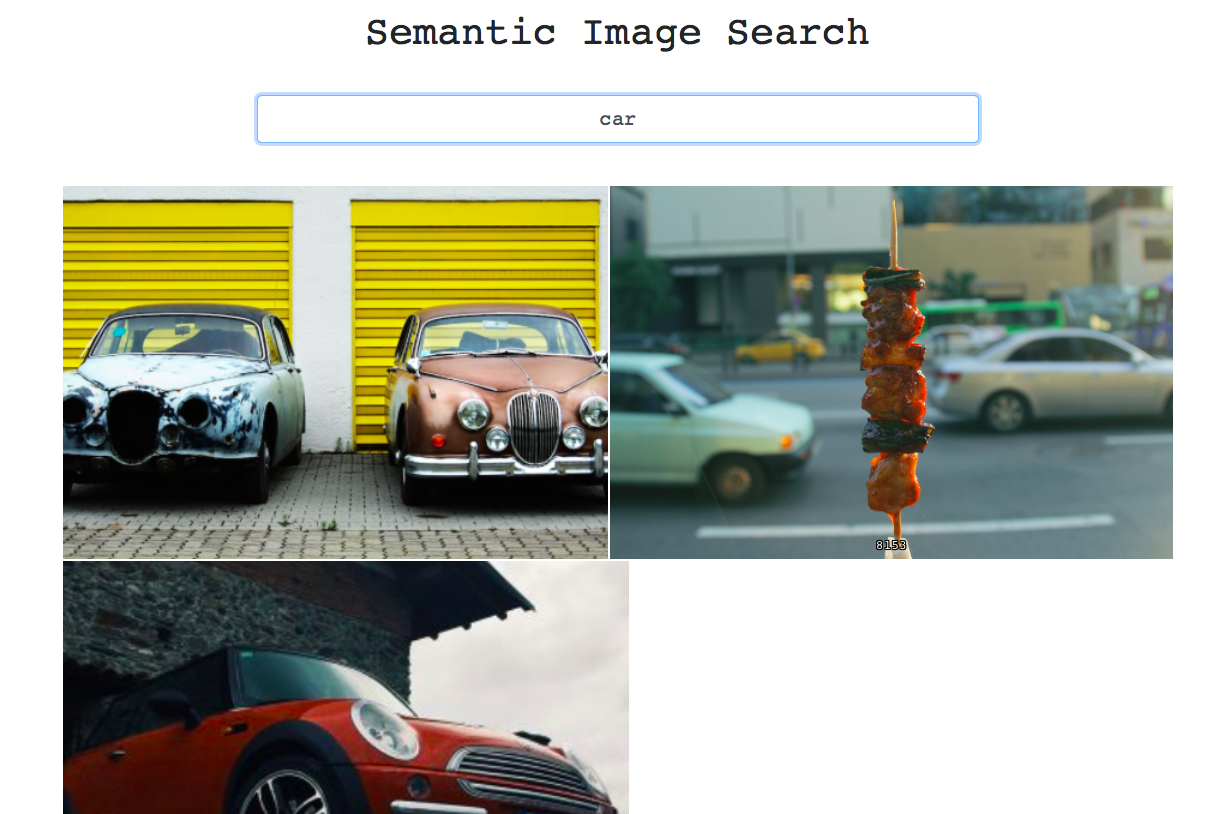
Conclusion
Using very few API calls, we were able to create the cool project. The source code of the project is available here for your reference. The last but not least the project is hosted in this page.