on
Summary of FCN paper
Paper
- Title: Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation(FCN)
- Submission date: 14 Nov 2014
Achievements
The FCN models are tested on the following datasets, the results reported are compared to the previous state-of-the-art methods.
- PASCAL VOC 2012
- achieved the best results on mean intersection over union (IoU) by a relative margin of 20%
- NYUDv2 dataset
- achieved mean IoU by 18.8% relative improvement
- SIFT Flow dataset
- achieved the best results on pixel accuracy by a relative margin of 8.39%
Key Contributions
This paper introduced the idea of converting classification networks into fully convolutional networks that produce coarse outputs. Then these coarse outputs are connected to dense pixels for pixelwise prediction.
The ideas the authors used in improving semantic segmentation are follows
- Adapting Classifiers for dense prediction
- Upsampling using deconvolution
Architecture
This paper cast the Imagenet classifiers into fully convolutional layers and augmented them with in-network upsampling and pixel-wise loss. The learned representation of Imagenet classifiers are fine-tuned for semantic segmentation.
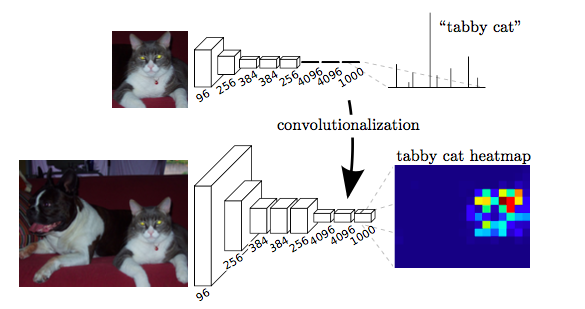
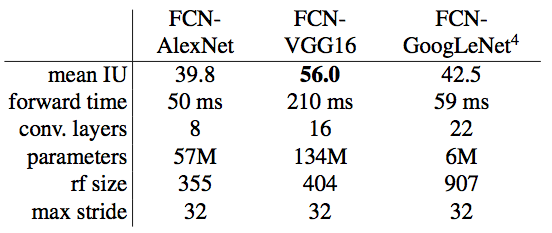
Authors adapted and extended the then best classfication networks on Imagenet. They compared the performance of each network by inference time and mean IoU on the validation set of PASCAL VOC.
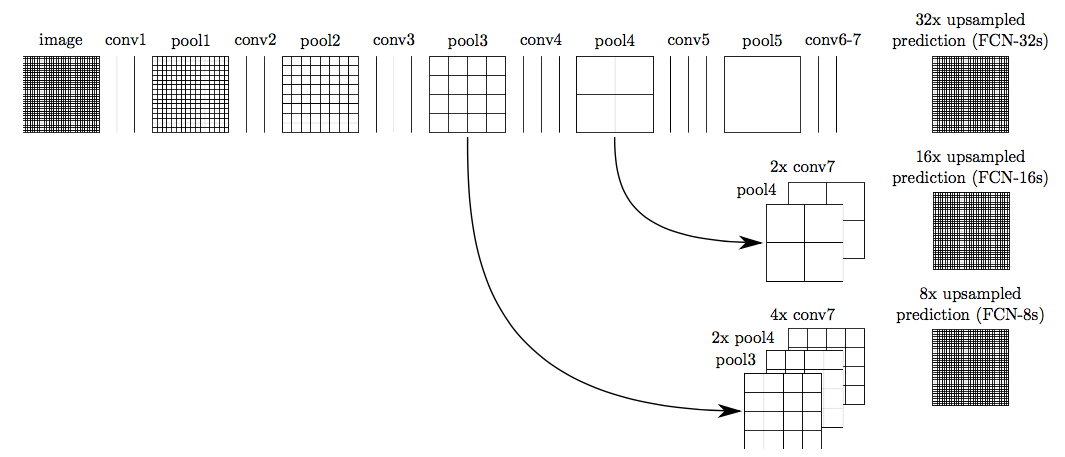
The 32 pixel stride at the final prediction layer (of unmodified classfication networks) limits the scale of detail in the upsampled output. They addresed this issue by adding skips between layers to fuse coarse, semantic information and fine, location information. See the architecture below: FCN-32, FCN-16 and FCN-8 architectures have stride of 32, 16 and 8 respectively.
Conclusion
Extending the classification networks to semantic segmentation, and modifying these architectures with multi-resolution layer combinations dramatically improved the then state-of-the-art results.