on
Summary of DeepLabv3 paper
Paper
- Title: Rethinking Atrous Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation (DeepLabv3)
- Submission date: 17 Jun 2017
Achievements
- The proposed ‘DeepLabv3’ system in this paper significantly improves over previous DeepLab versions without DenseCRF post-processing.
- Attains comparable performance with other state-of-art models on the PASCAL VOC 2012 semantic image segmentation benchmark.
Key contributions
- The authors revisited atrous convolution, a powerful tool to
- Adjust filter’s field-of-view to incorporate multi-scale context.
- Control the resolution of feature responses computed of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks(DCNNs).
- This paper is very well written.
Atrous convolution in the current work
The two challenges in applying DCNNs for semantic segmentation are
- Reduced feature resolution caused by consecutive pooling operations or convolution striding
- Existence of objects at multiple scales.
Atrous convolution is also known as dilated convolutions. It allows repurposing ImageNet pretrained Networks to extract denser feature maps by removing the downsampling operations from the last few layers and upsampling the corresponding filter kernels, equivalent to inserting holes between filter weights. With atrous convolution, we can able to control the resolution at which feature responses are computed within DCNNs without requiring to learn extra parameters.
Atrous rate say r is defined as convolving the feature input with upsampled filters produced by inserting r - 1 zeros between two consecutive filter values. Standard convolution is a special case for rate r = 1. Employing larger value of atrous rate enlarges the model’s field-of-view, enabling object encoding at multiple scales.
Atrous convolution also allows to explicitly control how densely to compute feature responses in fully convolutional networks. Output stride is defined as the ratio of input image spatial resolution to final output resolution.
To handle objects at multiple scales in the semantic segmentation, authors considered four categories of architectures in this paper.
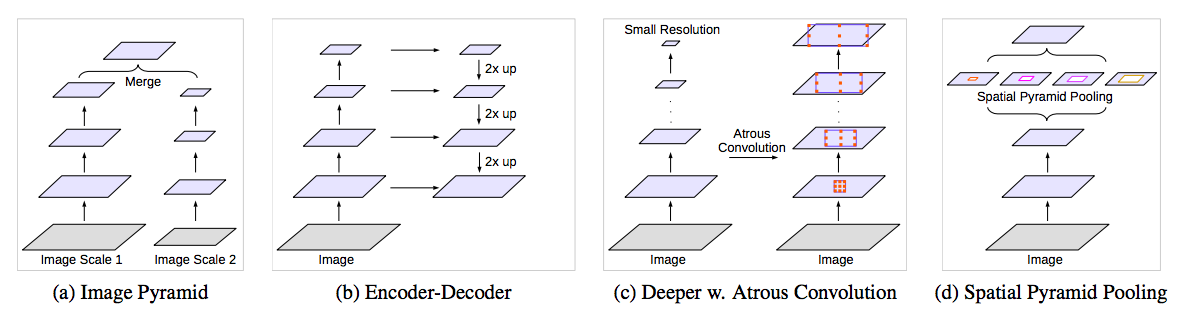
-
Image Pyramid: The DCNN is applied to an image pyramid to extract features for each scale input, where objects at different scales become prominent at different feature maps. Feature responses from the small scale inputs encode the long-range context, while the large scale inputs preserve the small object details. The main drawback of this type of models is that it does not scale well for larger/deeper DCNNs due to limited GPU memory.
-
Encoder-decoder: The encoder-decoder structure exploits multi-scale features from the encoder part and recovers the spatial resolution in the decoder part.
-
Context module: Extra-modules are cascaded on top of the original network for capturing long-range information. One effective method is to incorporate DenseCRF to DCNNs.
-
Spatial pyramid pooling: This model probes incoming feature map with filters or pooling operations at multiple rates and multiple effective field-of-views, thus capturing objects at multiple scales.
In this paper, authors mainly explored atrous convolution as a context module and tool for spatial pyramid pooling.
Results
Authors experimented with the modules employing Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (ASPP) method in cascade as well as in parallel. In experiments, the performance of the models was measured using Intersection Over Union (IOU). Based on validation set, the best model with ASPP attains the performance of 79.77%, better than the best model with cascaded atrous convolution modules (79.35%). Therefore ASPP was selected as final model for test set evaluation.
| Method | mIOU |
|---|---|
| DeepLabv3-JFT | 86.9 |
| DeepLabv3 | 85.7 |
| DIS | 86.8 |
| CASIA_IVA_SDN | 86.6 |
| IDW-CNN | 86.3 |
| PSPNet | 85.4 |
| ResNet-38_MS_COCO | 84.9 |
| Multipath-RefineNet | 84.2 |
| Large Kernel Matters | 83.6 |
| TuSimple | 83.1 |
| Deep Layer Cascade (LC) | 82.7 |
| SegModel | 81.8 |
| HikSeg_COCO | 81.4 |
| CentraleSupelec Deep G-CRF | 80.2 |
| DeepLabv2-CRF | 79.7 |
| LRR 4x ResNet-CRF | 79.3 |
| Adelaide VeryDeep FCN VOC | 79.1 |
The above table represents the method used and corresponding PASCAL VOC 2012 test set performance. From this, it is evident that ‘DeepLabv3’ achieves a performance of 85.7% which outperformed the previous DeepLab versions. DeepLabv3-JFT model was built using ResNet-101 model which has been pretrained on both ImageNet and JFT-300M dataset. This resulted a performance of 86.9% and shows a improvement compared to previous state-of-art methods.