on
Summary of Dilated Convolutions Paper
Paper
- Title: Multi-Scale Context Aggregation by Dilated Convolutions (Dilated Convolutions)
- Submission date: 23 Nov 2015
Key contributions
- Developed a convolutional newtork model especially designed for semantic segmentation.
- The main idea of the network was using dilated convolutions to aggregate multi scale contextual information without losing resolution of the input.
- This network neither uses pooling nor subsampling.
- Addressed the following questions
- Which aspects of the adapted networks are truly necessary and which reduce accuracy when operated densely?
- Can dedicated networks designed specially for semantic segmentation improve accuracy further?
Achievements
- The newly proposed network has a significant increase in the accuracy when compared with earlier state-of-the-art networks.
Dilated Convolutions in semantic segmentation
The goal of semantic segmentation is classifying each pixel of the input image into a given set of classes. The main challenge of this is to combine pixel level accuracy with multi scale contextual information. The previous state of the art models are based on the adaptations of convolutional neural networks designed for image classification.
The authors developed a new convolutional architecture that systematically uses dilated convolutions for multi-scale context aggregation. This idea was motivated by the fact that dilated convolutions support exponential expansion of receptive field without losing resolution as well as coverage.
Front End prediction module
This module is modified version of adapted VGG-16 network for semantic segmentation by removing the last two pooling and striding layers. Each of these pooling and striding layers was removed and convolutions in all subsequent layers were dilated by a factor of 2 for each pooling layer that was removed. The front-end prediction module was compared with FCN-8 and DeepLab(2015). The obtained results proved that front-end prediction module is both simpler and more accurate.
Context module
This module increases the performance by aggregating multi-scale contextual information. The architecture of this module is described in the below table.
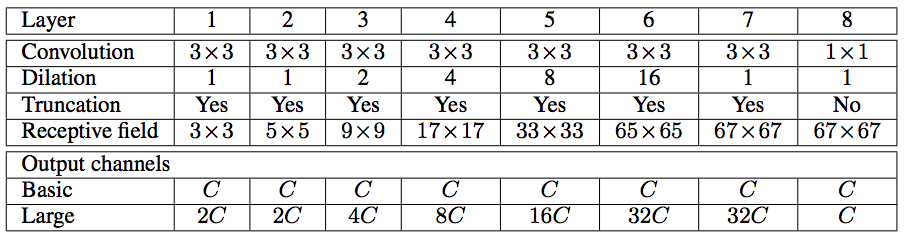
The above describes two types of architecture, i.e. basic and larger context network which maintains constant and larger number of feature maps correspondingly. These networks processes the given feature maps by aggregating contextual information at increasing scales.
Experiments are conducted by plugging basic and larger context module into front-end. These are evaluated on the PASCAL VOC 2012 test set. The results demonstrated larger context module with front-end yields a significant boost in accuracy over the front-end alone. The below table demonstrates the results.
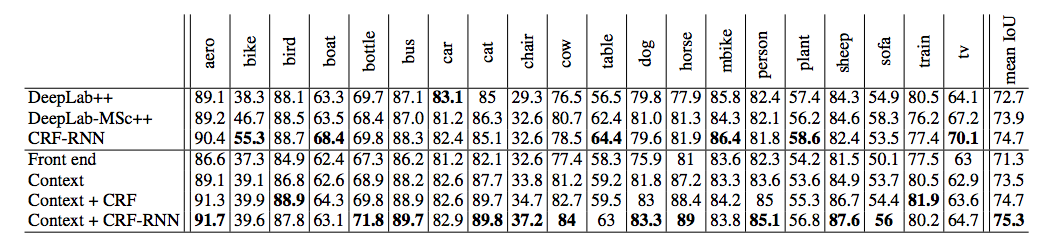
- DeepLab++ stands for DeepLab-CRF-COCO- LargeFOV
- DeepLab-MSc++ stands for DeepLab-MSc-CRF-LargeFOV-COCO-CrossJoint
- CRF-RNN is used for structured prediction
- Context refers to large context module plugged into our front end
Thus the context network was outperforming the DeepLab++ architecture without performing structured prediction. Combining the context network with the CRF-RNN structured prediction module improves the accuracy of the CRF-RNN system.