on
Summary of Faster R-CNN Paper
Paper
- Title: Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks (fasterRCNN)
- Submission date: 4 jun 2015
Key Contributions
- Introduced a region proposal network (RPN) that shares full-image convolutional features with detection network (Fast R-CNN), thus enabling cost-free region proposals.
- RPN and Fast R-CNN networks are merged into a single network and trained end to end. RPN component essentially tells the unified network where to look.
Achievements
- For the very deep VGG-16 model, end-to-end detection system has a frame rate of 5fps (including all steps) on a GPU.
- In ILSVRC and COCO 2015 competitions, Faster R-CNN and RPN are the basis of several 1st-place entries in the tracks of Imagenet detection, Imagenet localization, COCO detection, and COCO segmentation.
Object detection networks
Then advanced object detection networks depended on the following two steps.
- Region proposal module to hypothesize object locations in a image.
- Region based detectors which classify the above proposed object locations.
The previous state-of-the-art object detection networks like SPPnet and Fast R-CNN reduced their running time, exposing region proposal computation as a bottleneck.
The authors of this paper observed that convolutional feature maps used by region based detectors, like Fast R-CNN can also be used for generating region proposals. Then they introduced Region Proposal Networks (RPNs) that share convolutional layers with the state-of-the-art object detection network (Fast R-CNN). Thus RPN is a fully convolutional network that simultaneously predicts object bounds and object scores at each position. Now proposal computation is nearly a cost-free given the detection network’s computation.
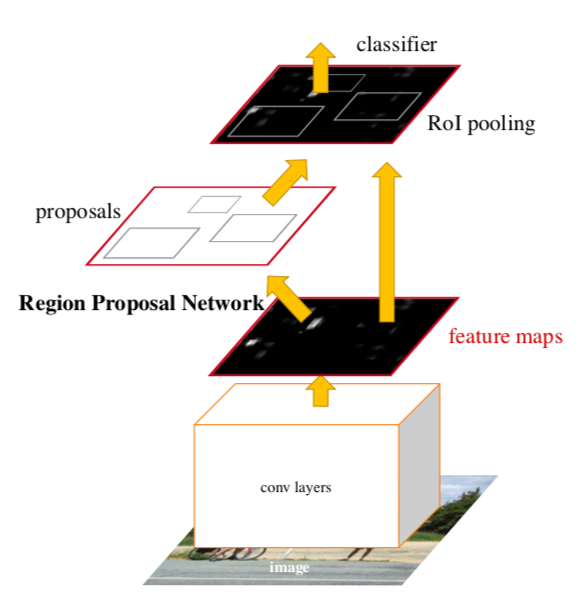
Faster R-CNN
Faster R-CNN network is a single and unified network for object detection. It consists of the following two modules.
- Deep fully convolutional network that proposes regions (RPN).
- Second module is the Fast R-CNN detector that uses the proposed regions.
Anchor boxes
Authors introduced novel “anchor” boxes that serve as references in generating region proposals. To generate region proposals, slide a small network over the convolutional feature map output by last convolutional layer of RPN (refer below figure).
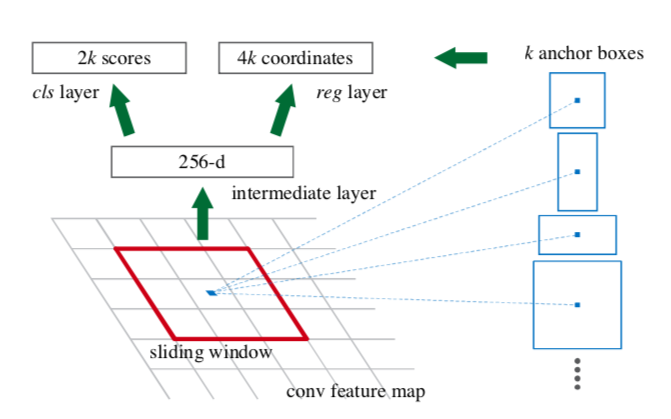
This small network takes an input n x n spatial window (red box in above figure) of the input feature map. Each sliding window is mapped to a lower dimensional feature (here intermediate layer - 256d). This feature is fed into two sibling fully-connected layers
- A box regression layer (reg)
- A box classification layer (cls).
At each sliding-window location, we simultaneously predict multiple region proposals, where the number of maximum possible proposals for each location is denoted as k (blue boxes).
- Now the reg layer has 4k outputs encoding the coordinates of k boxes
- The cls layer outputs 2k scores that estimate probability of object or not.
Therefore anchor is centered at the sliding window and is associated with scale and aspect ratio. For a convolutional feature map of a size W x H, there are \(W*H*k\) anchors in total.
Experiments
To unify RPNs with Fast R-CNN object detection networks, authors proposed a training scheme that alternates between fine-tuning for the region proposal task and then fine-tuning for object detection, while keeping the proposals fixed. This scheme converges quickly and produces a unified network with convolutional features that are shared between both tasks.
The following are the results of the experiments in the paper
- RPNs with Fast R-CNN produce detection accuracy better than the strong baseline of selective-search with Fast R-CNNs.
- Faster R-CNN method waives nearly all computational burdens of selective-search (a Region proposal method used in Fast R-CNN) at test-time, the effective running-time for proposals is just 10 milliseconds.
- Though using expensive very deep models, Faster R-CNN detection method still has a frame rate of 5fps (including all steps) on a GPU, and thus is a practical object detecion system in terms of both speed and accuracy. region-wise fully connected layers cost.